Treatment for Thin Skin and Easy Bruising

Skin discoloration is a common health issue that takes place when your skin begins to change color due to a medical condition or something in your environment that irritates it. In some cases, discoloration can be benign, or harmless. In other cases, it can mean you have an underlying disease or health condition that requires treatment. In this article, we'll take a look at some of the most common causes of skin discoloration, along with some of their treatments.
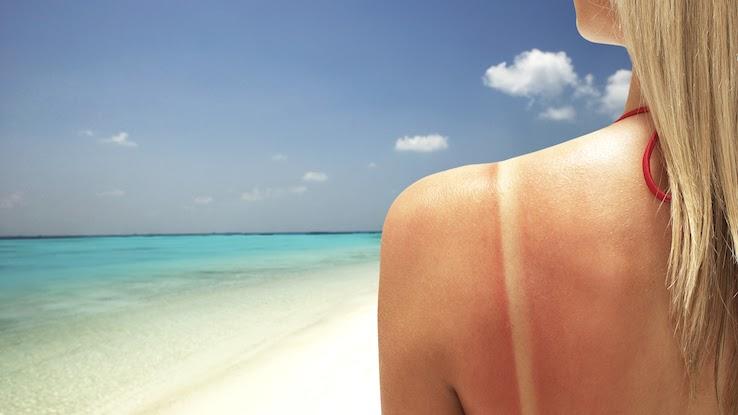
When your skin is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun, it can become red and inflamed. If you don't cover up or apply sunscreen, this inflammation can result in sun damage or sunburns, which can cause further redness and inflammation and make your skin start peeling. During this time, pigments in your skin rush to the damaged areas to shield them from UV rays.
Jaundice – Yellow Skin
Jaundice of the skin often happens to infants during their first two weeks of life. It causes your skin and the whites of your eyes to develop a yellowish cast. This condition is usually temporary and can sometimes resolve on its own. However, a doctor can also treat it easily. Sometimes, jaundice in adults may indicate a more severe health condition like liver failure.
Vitiligo – White Patches
This non-contagious skin condition occurs due to the death of melanocytes — our skin's color-producing pigments. Symptoms include patches of light colored skin that typically don't cause itching or scaling. Vitiligo can develop if you have an autoimmune or hormone disorder. Be sure to see a healthcare provider if you start to experience these characteristic white patches.
Scar Discoloration – Concentrated Dark Areas
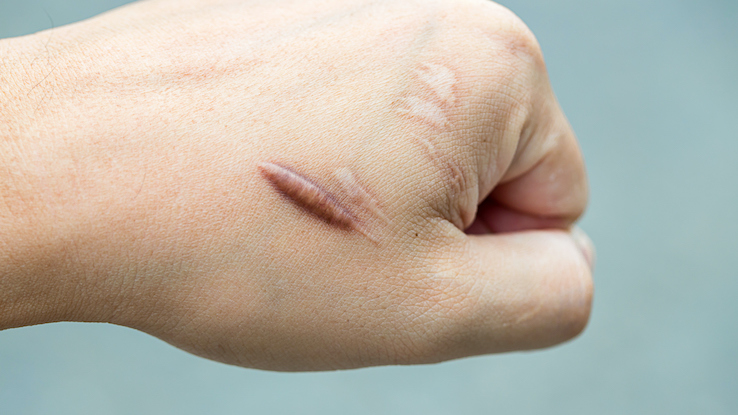
Skin typically develops redness and discolored areas during the healing process after an injury or some type of irritation. Scarring, including that due to surgeries, injuries, acne scars and even bug bites, can darken if you don't take certain steps during the healing process. To avoid discolored scarring, limit your sun exposure and moisturize diligently.
Rosacea – Red, Flushed Skin
The symptoms of rosacea can range from flushed skin with small, dilated blood vessels to rough patches with small bumps. There are many potential causes for this condition, so it's best to see a doctor if you notice redness that doesn't fade. They can help you get relief from your symptoms and rule out any potential autoimmune conditions.
Cirrhosis – Small Blood Vessels
Some medical conditions unrelated to your skin can still cause you to develop small, spider web-like blood vessels on your skin as a symptom. One of these conditions is cirrhosis. This causes scarring of the liver and usually develops due to excess alcohol consumption or chronic hepatitis C. It's important to see a doctor if you think you have cirrhosis to prevent the condition from worsening.
Cyanosis – Blue-Tinted Skin
Having bluish lips, fingernails or skin usually means you don't have enough oxygen in your blood. This condition is known as cyanosis, and it can develop slowly or suddenly. Cyanosis can mean you have underlying problems with your lungs (such as chronic lung disease or drowning) or your heart (such as heart defects, blood clots or heart failure). Be sure to see a doctor if you notice a bluish tinge in your extremities or lips.
Birthmarks – Varying Shapes and Colors
Birthmarks can vary in size and color, and they can appear anywhere on your skin. Some harmless birthmarks may fade as a baby grows larger, but most stay for the duration of a person's lifetime. While most birthmarks are harmless, you might ask your doctor about removing them if they affect your self-esteem or quality of life.
Hormone Imbalance – Dark Patches
If you're experiencing dark patches on your face or the areas of skin around your joints, it may be due to hormonal changes in your body. If you're not pregnant and have patches of dark, leathery or uneven skin, you may want to see a doctor. This may be acanthosis nigricans, which is associated with insulin resistance.
Infection – Multicolored Discoloration
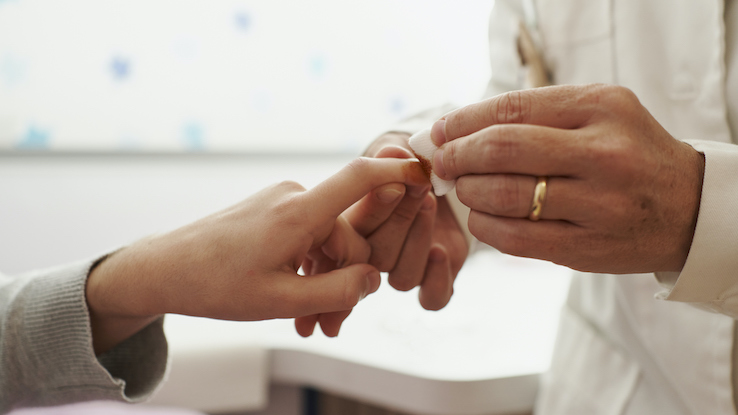

After you get a skin wound, your skin is susceptible to infection from bacteria. These infections often cause the wounded area to appear red and swollen, and they may produce pus. Viral infections may also cause rashes on your skin. Be sure to see your doctor as soon as possible; skin infections are usually very treatable in their early stages.
Resource Links:
"Skin – abnormally dark or light Information," Mount Sinai
"Skin Discoloration & Hyperpigmentation," Affiliated Dermatology
"Skin Discoloration & Pigmentation Disorders: Causes & Treatments," Cleveland Clinic
bowlintruckly1955.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.symptomfind.com/beauty-wellness/causes-skin-discoloration?utm_content=params%3Ao%3D740013%26ad%3DdirN%26qo%3DserpIndex&ueid=57296d9d-5990-4813-a26e-eea57a0a7c5d

Post a Comment for "Treatment for Thin Skin and Easy Bruising"